As temperatures in the Arctic plummet to -50°C and ice sheets stretch endlessly, the Yamal nuclear icebreaker has emerged as a symbol of human adaptation and technological advancement. Over three decades, this vessel has achieved a legendary status in a realm known for its extreme challenges, particularly in maritime navigation.
From Cold War Necessity to Arctic Innovation
The inception of the Yamal dates back to the 1970s, a critical era for the Soviet Union confronted with strategic imperatives. The Northern Sea Route (NSR), which runs along Russia’s Arctic coastline from the Barents Sea to the Bering Strait, was recognized not only as an essential economic channel but also as a fundamental military asset. Diesel-powered icebreakers at that time were deemed inadequate for ensuring year-round navigation through these frozen waters, primarily due to their limited fuel capacity and the frequent need for refueling. This made prolonged Arctic missions particularly challenging during the brutal winter months.
Dr. Viktor Petrov, a maritime historian at the Russian Arctic Institute, underscores the significance of this endeavor, stating, “The Northern Sea Route was crucial for Soviet development. The decision to develop nuclear-powered icebreakers wasn’t just about prestige – it was about survival and sovereignty in the Arctic region.”
Engineering Challenges in the Arctic Frontier
The Yamal, part of the distinguished Arktika-class of nuclear icebreakers, posed significant engineering hurdles. The Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute in Leningrad undertook the formidable task of incorporating nuclear propulsion into a vessel designed to operate in one of the world’s most extreme maritime environments.
Nuclear Innovation at Sea
At the core of the Yamal are two OK-900A pressurized water reactors, each capable of delivering 171 megawatts of propulsion power. The unique challenge lay in the installation of these reactors within a vessel that would routinely navigate through ice barriers, necessitating innovative engineering solutions.
The design team focused on developing specialized containment systems aimed at shielding the crew from radiation, all while minimizing the impact on overall vessel performance. The reactor shielding itself represented a considerable engineering milestone, necessitating the use of new materials and designs capable of withstanding the constant stress from ice impacts.
Through these advancements, the Yamal not only exemplifies a leap in maritime technology but also reflects the broader narrative of human ingenuity in overcoming environmental and technical challenges.
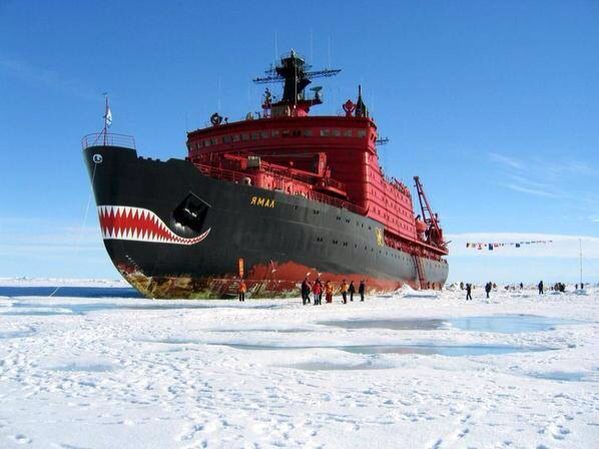
Breaking the Ice Ceiling: The Yamal Icebreaker
The Yamal, a state-of-the-art nuclear icebreaker, features a distinctive spoon-shaped bow that was developed through comprehensive hydrodynamic testing and theoretical modeling. Unlike conventional icebreaker vessels, the Yamal’s design allows it to ride up onto ice sheets, utilizing its substantial displacement of 23,000 tons to effectively crush through ice barriers measuring up to 2.3 meters thick.
The vessel boasts several innovative design elements, including:
– A reinforced double-hull structure with specialized ice-belt reinforcement.
– Three fixed-pitch propellers optimized for maximum thrust in icy conditions.
– An advanced air bubbling system that diminishes ice friction during operations.
– Cutting-edge ice-thickness monitoring systems to enhance navigational safety.
Building the Arctic Giant
The construction of the Yamal commenced in 1986 at the Baltic Shipyard in Leningrad, present-day St. Petersburg. This shipyard is among the few globally recognized facilities capable of fabricating nuclear-powered vessels. Throughout the construction process, the team encountered a myriad of technical and logistical obstacles.
The double-hull design was particularly challenging, demanding extraordinary precision in welding. Over 200 kilometers of welds were completed, with each requiring X-ray verification to ensure integrity. Additionally, new grades of steel were created specifically to withstand Arctic conditions, maintaining structural integrity at extreme temperatures while providing essential strength for ice operations.
Technical Specifications That Define Excellence
The Yamal’s notable specifications are indicative of its status as a significant achievement in maritime engineering:
– Length: 150 meters (492 feet)
– Beam: 30 meters (98 feet)
– Draft: 11 meters (36 feet)
– Displacement: 23,000 tons
– Maximum Speed: 20.8 knots in open water
– Ice-breaking Capability: Able to progress continuously through 2.3-meter thick ice
The specifications of the Yamal’s nuclear power plant further highlight the vessel’s advanced technological framework:
– Reactor Type: OK-900A pressurized water reactors
– Thermal Power: 171 megawatts per reactor
– Core Life: 4 to 5 years between refueling
– Emergency Systems: Designed with triple redundancy
– Total Shaft Power: 75,000 horsepower
Surviving Political Upheaval: The Yamal Icebreaker
One of the most notable aspects of the Yamal icebreaker’s history is its completion during the tumultuous period surrounding the dissolution of the Soviet Union. As the political and economic fabric of the nation unraveled, the strategic significance of the Yamal project played a critical role in its survival. Commissioned in 1992, the vessel stands as one of the few large-scale Soviet engineering endeavors that successfully transitioned into the era of the Russian Federation.
Operational Excellence, Environmental Impact, and Arctic Legacy
The Yamal’s influence on Arctic navigation extends well beyond its remarkable technical specifications. With over three decades of operational experience, this nuclear-powered vessel has significantly shaped the understanding of polar maritime operations while adapting to the changing demands of the Arctic environment.
Mastering the Arctic Environment
The Yamal is easily recognizable by its distinctive shark-faced bow, adorned with intimidating teeth that have made it an iconic presence in polar waters. However, this aesthetic feature conceals the advanced technology that allows the vessel to excel in harsh Arctic conditions. Some of the sophisticated ice-navigation systems integrated into the Yamal include:
– Dual-band radar systems optimized for effective ice detection
– Thermal imaging equipment designed for navigation in polar darkness
– Real-time satellite ice monitoring for improved safety and efficiency
– Advanced ice-load monitoring systems that enhance operational capabilities
Captain Mikhail Kozlov, a seasoned navigator in Arctic waters, emphasizes the Yamal’s unique capabilities: “What makes the Yamal exceptional isn’t just its raw power. It’s the vessel’s ability to read ice conditions and adapt its breaking strategies accordingly. In the Arctic, understanding ice is as crucial as having the power to break it.”
Operational Achievements of the Yamal Icebreaker
Since its commissioning, the Yamal icebreaker has established a noteworthy operational record. This includes more than 50 successful expeditions to the North Pole, extended operations lasting up to 7.5 months without port calls, and the capability to navigate through ice fields exceeding 2 meters in thickness during the winter months. Additionally, the Yamal has played a significant role in supporting numerous critical scientific missions in the Arctic region.
The vessel’s nuclear propulsion system has proven particularly beneficial during extended missions in the Arctic, enabling the Yamal to operate for years without refueling. This critical feature offers a level of reliability that is essential for operations in the remote polar environments.
Beyond Ice-Breaking: Evolving Missions
Originally conceived to maintain shipping lanes through the Northern Sea Route, the Yamal icebreaker has adapted to fulfill multiple roles within the Arctic region:
Scientific Platform
The Yamal regularly hosts international research teams engaged in studying various aspects of the Arctic environment, including:
– Patterns of climate change in the Arctic region
– Dynamics of marine ecosystems
– Ice formation and movement
– Collection of oceanographic data
Arctic Tourism Pioneer
In a strategic initiative aimed at financing operations, the Yamal has commenced tourist expeditions to the North Pole. These missions provide civilians with unique opportunities to experience the High Arctic, while also contributing to the vessel’s operational sustainability.
Emergency Response Asset
The capabilities of the Yamal make it an invaluable asset for emergency response efforts in the Arctic. The vessel is equipped to:
– Break through ice to reach stranded vessels
– Provide emergency power to coastal communities
– Support search and rescue operations
– Deliver essential supplies to remote Arctic settlements
Navigating a Changing Arctic
The Yamal icebreaker, equipped with a nuclear propulsion system, presents a significant opportunity for reducing carbon emissions in the Arctic. However, the operation of such a vessel also requires meticulous management of nuclear fuel and waste. Dr. Elena Volkova, an environmental scientist specializing in Arctic operations, emphasizes the inherent complexities: “Nuclear-powered icebreakers like the Yamal represent a delicate environmental balance. Their zero-emission operation is vital for protecting the fragile Arctic ecosystems, but stringent nuclear safety protocols are paramount.”
To address these challenges, the Yamal employs comprehensive environmental impact mitigation measures, including:
– Advanced Radiation Monitoring Systems: These systems ensure the safety of both the crew and the surrounding environment.
– Stringent Waste Management Protocols: Designed to minimize the impact of nuclear waste, these protocols are critical for environmental protection.
– Regular Environmental Impact Assessments: These assessments monitor the vessel’s ecological footprint, helping to mitigate negative effects.
– Continuous Monitoring of Marine Ecosystems: This practice allows for the detection and mitigation of any potential adverse effects on the Arctic environment.
A Legacy of Innovation: Shaping Modern Arctic Navigation
The enduring success of the Yamal has had a profound impact on the design and construction of subsequent icebreakers. Key areas of advancement include:
Technical Advancements
– Enhanced Automation Systems: These systems contribute to safer and more efficient ice navigation.
– Improved Nuclear Propulsion Efficiency: The Yamal’s propulsion system supports extended operational ranges while reducing environmental impact.
– Advanced Hull Design Concepts: Optimized for ice breaking performance and maneuverability, these designs enhance operational effectiveness.
– Sophisticated Ice-Monitoring Technologies: Such technologies improve situational awareness and risk mitigation during operations.
Operational Procedures
– Standardized Arctic Navigation Protocols: These protocols are essential for increasing safety and operational efficiency in Arctic conditions.
– Improved Crew Training Methodologies: Enhanced training programs cultivate expertise and readiness among crew members.
– Enhanced Safety Procedures: Particularly for nuclear vessels, these procedures prioritize the well-being of both crew and the environment.
– Efficient Ice-Breaking Techniques: Innovations in this area lead to reduced fuel consumption and a corresponding decrease in environmental impact.
Future Implications
As climate change reshapes the Arctic landscape, the importance of vessels like the Yamal continues to grow. Increased maritime traffic through the Northern Sea Route demands reliable ice-breaking capabilities, while changing ice conditions require adaptable vessel designs.
The lessons learned from the Yamal’s operation are already influencing the next generation of Arctic vessels, including Russia’s LK-60Ya class nuclear icebreakers. These new vessels incorporate many innovations pioneered by the Yamal while adapting to emerging Arctic challenges.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Arctic Innovation
The Yamal icebreaker signifies more than just an engineering marvel; it embodies human ingenuity in addressing some of the most extreme environmental challenges. With three decades of successful operation, the Yamal has demonstrated the feasibility of nuclear-powered vessels in Arctic waters and has established pioneering standards for polar maritime operations. As shipping lanes in the Arctic increasingly play a crucial role in global commerce, the legacy of the Yamal continues to shape the future of navigation in this sensitive region.
The vessel’s robust engineering, operational versatility, and commitment to environmental stewardship serve as a comprehensive blueprint for sustainable maritime operations in the Arctic region moving forward. Captain Kozlov articulates this sentiment, stating, “The Yamal’s greatest contribution might be showing us what’s possible in Arctic navigation. It proved that with the right combination of engineering, technology, and human expertise, we can reliably operate in the world’s most challenging maritime environment.”
The insights presented in this article draw upon operational records, environmental assessments, and expert commentary regarding the Yamal’s impact on Arctic navigation. While efforts have been made to ensure the accuracy of information, it is noted that certain operational details may have been modified over time for reasons pertaining to security or technical considerations.



Leave a reply to Seafaring in the Arctic: Tales of Ice and Survival Adventures – Seafaring History Cancel reply